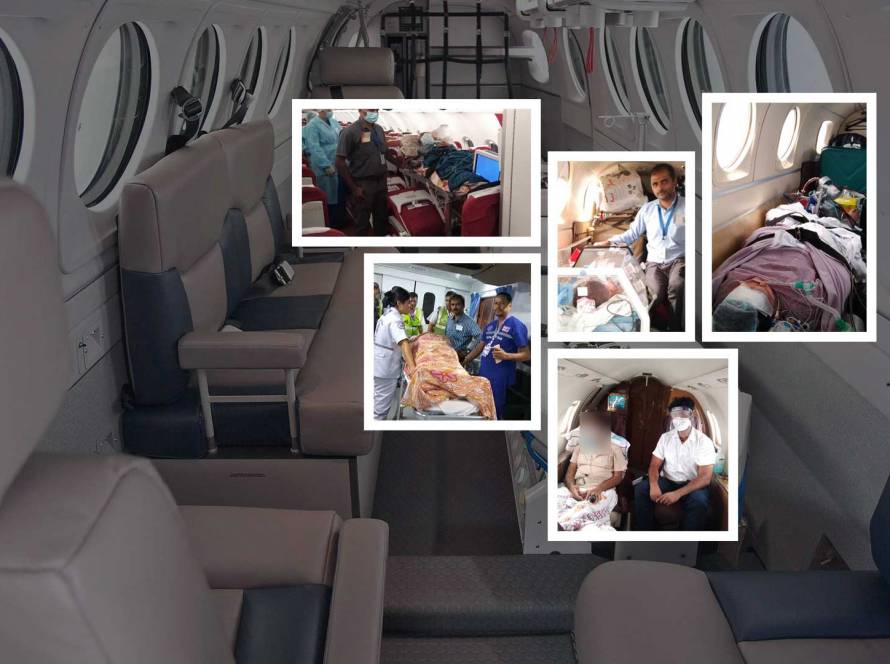
When a patient needs to travel internationally for medical reasons, the journey must be more than just fast — it must be safe, medically equipped, and tailored to their condition. This is where International Commercial Stretcher Services step in as a life-saving bridge between care facilities, families, and better health outcomes.
An international commercial stretcher service allows patients who are medically stable — but cannot sit upright during a flight — to be transported across countries using a commercial airline. A section of the plane is converted into a private, secure stretcher space, complete with medical monitoring and professional care throughout the flight.
Who Can Benefit from Commercial Stretcher Services?
-
Patients recovering from major surgery
-
Individuals with spinal injuries or severe mobility limitations
-
Those needing medical repatriation
-
Seniors who are non-ambulatory but need to travel internationally
-
Patients requiring long-distance transport to specialized treatment centers
What’s Included in the Service?
-
Stretcher installation onboard a commercial airline (approved and coordinated with the airline)
-
Experienced medical escorts including nurses, paramedics, or physicians
-
Coordination with hospitals at both origin and destination
-
Oxygen support, cardiac monitoring, medications, and other necessary medical equipment
-
24/7 case management and logistics coordination
Why Choose a Commercial Stretcher Service?
-
Cost-effective alternative to full air ambulance charters
-
Global coverage with seamless planning and support
-
Dedicated medical team ensuring continuous care
-
Comfort and dignity for patients and peace of mind for families
-
Faster repatriation or access to urgent treatment
in organizing and executing safe international stretcher services. Our expert team handles all logistics — from airline negotiations to medical readiness — so your loved one can travel safely and comfortably.
Whether you’re arranging a transfer from India to the USA, Canada, the UK, or any global destination, MedEscort is here to help every step of the way
Contact Us:
If you or a loved one require Medical Escort Services or air ambulance transportation for safe, efficient, and compassionate care.
Call Us: +919774900430
Email: alan@medescortinternational.com
Address:HN-8/258 F/F Vilage Mehram Nagar Vasant Kunj Near Domestic, Airpo RT NEW, Delhi 110037